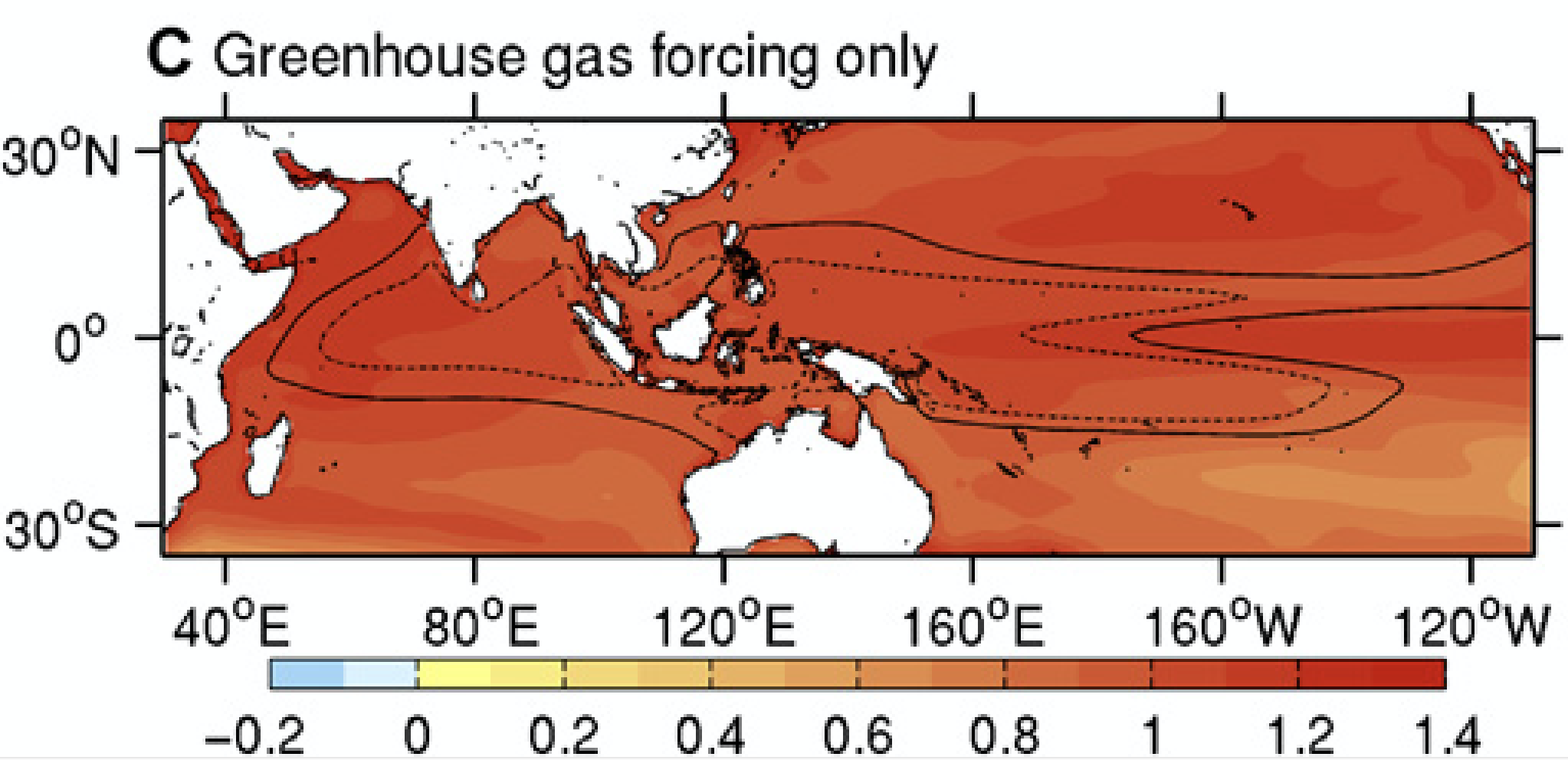
 The authors identify human and natural contributions to the observed Indo-Pacific warm pool (IPWP) changes since the 1950s by comparing observations with climate model simulations using an optimal fingerprinting technique. Greenhouse gas forcing is found to be the dominant cause of the observed increases in IPWP intensity and size, whereas natural fluctuations associated with the Pacific Decadal Oscillation have played a smaller yet significant role.
The authors identify human and natural contributions to the observed Indo-Pacific warm pool (IPWP) changes since the 1950s by comparing observations with climate model simulations using an optimal fingerprinting technique. Greenhouse gas forcing is found to be the dominant cause of the observed increases in IPWP intensity and size, whereas natural fluctuations associated with the Pacific Decadal Oscillation have played a smaller yet significant role.
Human-caused Indo-Pacific warm pool expansion
- Details

